Day 2 - Module 5: Implementing Single Agents (ReAct Pattern)
Objective: Understand and implement the ReAct (Reason + Act) pattern to create autonomous agents that can use tools iteratively to solve problems.
Source Code: src/05-single-agent/
Introduction
Having explored how to equip LLMs with tools and structure their thinking (Module 4), we now focus on building agents that can autonomously decide which tools to use and when to use them to accomplish a given task. A popular pattern for this is ReAct (Reason + Act).
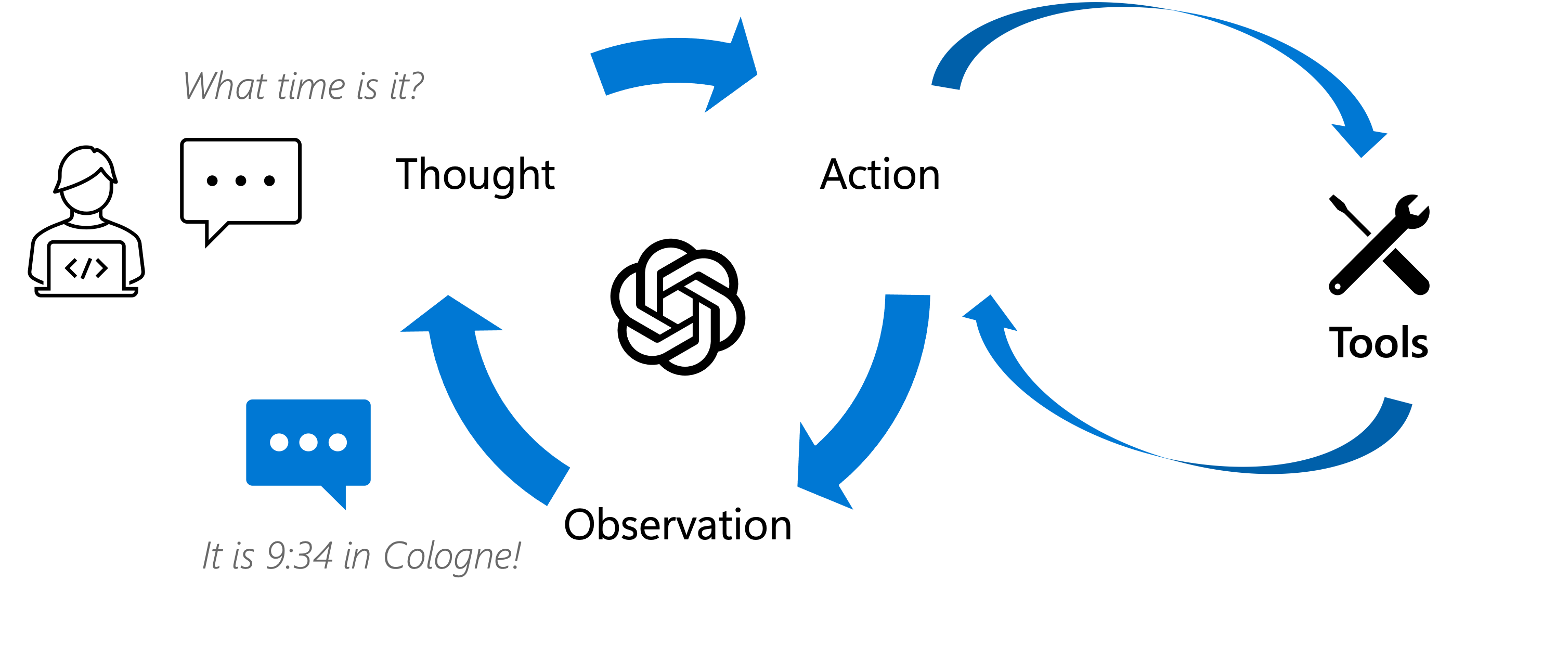
The ReAct pattern involves an iterative loop:
- Thought: The agent reasons about the current state, the overall goal, and what action is needed next.
- Action: The agent decides to use a specific tool.
- Action Input: The agent determines the necessary input for the chosen tool.
- Observation: The agent receives the result (output) from executing the tool.
- The agent incorporates the observation into its reasoning (back to step 1) and continues the loop until the final answer is determined.
This module demonstrates the ReAct pattern using three different frameworks:
- LangChain: Using
create_react_agentandAgentExecutor. - LlamaIndex: Using the
ReActAgentclass. - Semantic Kernel: Using
ChatCompletionAgentwith auto function calling (implicitly follows a similar reasoning loop).
All examples use a similar set of tools defined in plugins.py (for Semantic Kernel) or directly in the scripts (for LangChain/LlamaIndex) for getting user info, location, and time.
Shared Tools Concept
plugins.py(for Semantic Kernel): Defines aChefPluginclass with methods decorated by@kernel_function. These methods (get_weather,get_medical_history,get_available_incredients,get_current_username,get_current_location_of_user,get_current_time) become tools available to the Semantic Kernel agent.- LangChain/LlamaIndex Examples: Define similar functions (
get_current_username,get_current_location,get_current_time) and wrap them using framework-specific decorators or classes (@toolfor LangChain,FunctionTool.from_defaultsfor LlamaIndex) to make them usable by the respective agents.
1. ReAct with LangChain
File: src/05-single-agent/react-agent-lc.py
This script uses LangChain to create a ReAct agent.
Code Breakdown:
- Import Libraries:
langchain,langchain_openai, etc. - Initialize LLM: Sets up the
ChatOpenAIclient. - Define Tools: Uses the
@tooldecorator on Python functions (get_current_username,get_current_location,get_current_time) to make them LangChain tools. - Define ReAct Prompt Template:
- A specific prompt (
promptString) instructs the LLM on the ReAct process:- Explains the
Thought,Action,Action Input,Observationsequence. - Lists available tools (
{tools},{tool_names}). - Specifies the format for the final answer.
- Includes placeholders for the user input (
{input}) and the agent's internal scratchpad ({agent_scratchpad}).
- Explains the
PromptTemplate.from_template(promptString)creates the template object.
- A specific prompt (
- Create ReAct Agent:
create_react_agent(llm, tools, prompt)combines the LLM, tools, and the specific ReAct prompt. - Create Agent Executor:
agents.AgentExecutor(...)wraps the agent logic. It handles the execution loop:- Calls the agent to get the next action.
- Executes the action (tool).
- Passes the observation back to the agent.
- Repeats until the agent provides a final answer.
verbose=Trueshows the Thought/Action/Observation steps.handle_parsing_errors=Trueattempts to recover if the LLM output doesn't perfectly match the expected format.max_iterationsprevents infinite loops.
- Invoke Executor:
agent_executor.invoke({"input": input})starts the process with the user's question.
To Run:
cd /home/ubuntu/agentic-playground/src/05-single-agent
# Ensure langchain, langchain-openai, pytz are installed
python react-agent-lc.py
Observe the verbose output. You will see the agent's reasoning steps (Thought), the tools it chooses (Action), the inputs it provides (Action Input), and the results it gets back (Observation) as it works towards answering "What is the current time here?". It should first get the username, then the location, then the time for that location.
2. ReAct with LlamaIndex
File: src/05-single-agent/react-agent-li.py
This script implements the same ReAct logic using LlamaIndex.
Code Breakdown:
- Import Libraries:
llama_index.core.agent,llama_index.llms.openai,llama_index.core.tools, etc. - Define Tools: Uses
FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=...)to wrap the Python functions (get_current_username,get_current_location,get_current_time) into LlamaIndex tools. - Initialize LLM: Uses
OpenAILiketo connect to the GitHub Models endpoint (or standardOpenAIif configured differently). - Define ReAct System Prompt: Similar to LangChain, a detailed system prompt (
react_system_header_str) explains the Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation format and rules to the LLM.PromptTemplate(react_system_header_str)creates the template. - Create ReAct Agent:
ReActAgent.from_tools(...)creates the agent:- Takes the list of tools.
- Takes the LLM instance.
- Can optionally take a custom
react_chat_formatterand system prompt (the example relies on the default prompt structure expected byReActAgent; the commentedagent.update_promptsshows customization is possible). verbose=Trueenables detailed logging of the ReAct steps.
- Chat with Agent:
agent.stream_chat(...)initiates the conversation. LlamaIndex's ReAct agent handles the iterative tool use internally based on the prompt structure. - Stream Response: The example uses
response_gen.print_response_stream()to print the agent's thoughts and final answer as they are generated.
To Run:
cd /home/ubuntu/agentic-playground/src/05-single-agent
# Ensure llama-index, llama-index-llms-openai, pytz are installed
python react-agent-li.py
Again, observe the output stream. You should see the agent reasoning, selecting tools (get_current_username, get_current_location, get_current_time), executing them, and finally providing the answer.
3. Reasoning Agent with Semantic Kernel
File: src/05-single-agent/reasoning-agent-sk.py
This script uses Semantic Kernel's agent capabilities. While not explicitly called "ReAct" in the code, the ChatCompletionAgent with automatic function calling enabled achieves a similar iterative reasoning and tool-use loop.
Code Breakdown:
- Import Libraries:
semantic_kernel,semantic_kernel.agents,semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.open_ai, etc. - Import Plugin: Imports
ChefPluginfromplugins.py. - Create Kernel: A helper function
_create_kernel_with_chat_completionsets up a Semantic Kernel instance, adds theOpenAIChatCompletionservice, and crucially, adds theChefPlugin. - Configure Function Calling:
_create_chat_completion_clientgets the kernel and execution settings.execution_settings.function_choice_behavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto()tells the kernel/LLM to automatically decide when to call functions (tools) from the added plugin based on the conversation.
- Create Chat Completion Agent:
ChatCompletionAgent(...)creates the agent instance, providing the kernel (with the plugin and function calling enabled) and instructions. - Chat Loop:
- The
mainfunction runs an interactive loop. agent_expert.invoke(messages=user_input, thread=thread)sends the user message to the agent.- Semantic Kernel handles the interaction with the LLM. If the LLM decides a function call is needed (based on the prompt, history, and available functions in
ChefPlugin), the kernel executes it and sends the result back to the LLM to continue processing, mimicking the ReAct cycle. - The loop prints messages from the agent (which could be intermediate thoughts/tool calls if configured, or the final response).
- The
To Run:
cd /home/ubuntu/agentic-playground/src/05-single-agent
# Ensure semantic-kernel, pytz are installed
python reasoning-agent-sk.py
Enter the question "What is the current time here?" at the User:> prompt. Observe the output. While it does not explicitly show "Thought/Action/Observation" like the other frameworks by default, the agent will call get_current_username, get_current_location_of_user, and get_current_time from the ChefPlugin before giving the final answer, demonstrating the underlying reasoning and tool use.
This module introduced the ReAct pattern for building single autonomous agents using LangChain, LlamaIndex, and Semantic Kernel. The next module will explore how to introduce human oversight and intervention into agent workflows.