Day 1 - Module 1: Exercises
These exercises are based on the concepts and code presented in Module 1: Basic LLM Interaction & Tool Calling (src/01-basics/).
Exercise 1.1: Changing Language and Persona
Goal: Practice modifying the system prompt to change the LLM's behavior.
- Open the
src/01-basics/hello-world.pyscript. - Modify the
systemmessage content from "antworte alles in französisch" to instruct the model to respond like a pirate (e.g., "Answer everything like a pirate."). - Modify the
usermessage content to ask a different question (e.g., "What is the weather like today?"). - Run the script (
python hello-world.py) and observe the pirate-themed response.
Exercise 1.2: Using the Time Tool for a Different City
Goal: Practice changing the user input to trigger a tool call with different arguments.
- Open the
src/01-basics/tool-calling.pyscript. - Locate the initial
usermessage: - Change the
contentto ask for the time in a specific city, for example, Tokyo: "What time is it in Tokyo?". - Run the script (
python tool-calling.py). - Observe the output. Does the
get_current_timefunction get called withAsia/Tokyo(or a similar valid timezone identifier derived by the LLM)? Does the final model response include the correct time for Tokyo?
Exercise 1.3 (Advanced): Adding a Simple Calculator Tool
Goal: Practice defining and integrating a new tool for the LLM to use.
Tool calling allows the LLM to interact with external functions or APIs to retrieve information or perform actions. The diagram below illustrates the concept:
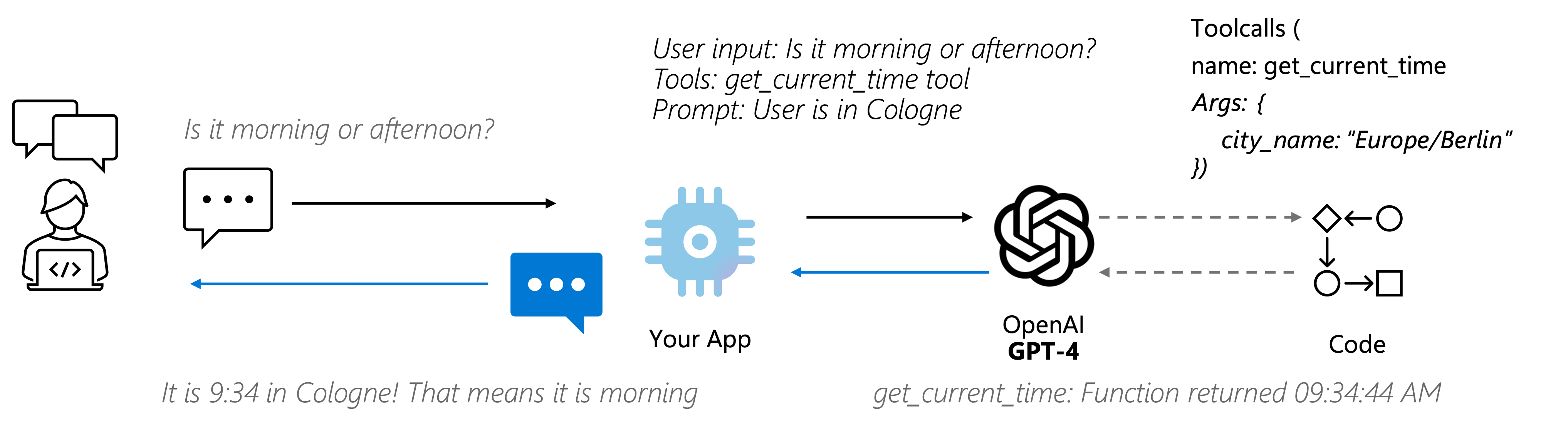
- Open the
src/01-basics/tool-calling.pyscript. - Define a new Python function: Add a function that performs simple addition.
- Define the tool schema: Create a new dictionary describing the
add_numbersfunction to the LLM, similar to theget_current_timeschema.add_tool = { "type": "function", "function": { "name": "add_numbers", "description": "Adds two integer numbers together.", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "a": { "type": "integer", "description": "The first number.", }, "b": { "type": "integer", "description": "The second number.", } }, "required": ["a", "b"], }, }, } - Update the API calls:
- Modify the
toolslist passed toclient.chat.completions.createto include both the original time tool (tool) and the newadd_tool: - Ensure this updated
toolslist is used in both the initial API call and the second call made after handling a potential tool invocation.
- Modify the
- Update the user query: Change the initial
usermessage to ask an addition question, e.g., "What is 123 plus 456?". - Run the script:
python3.11 tool-calling.py. - Observe the output. Does the LLM correctly identify the need for the
add_numberstool? Is the function called with the correct arguments? Does the final response contain the sum?